Graph RAG User Manual
In this example, we will show how to use the Graph RAG framework in DB-GPT. Using a graph database to implement RAG can, to some extent, alleviate the uncertainty and interpretability issues brought about by vector database retrieval.
You can refer to the python example file DB-GPT/examples/rag/graph_rag_example.py in the source code. This example demonstrates how to load knowledge from a document and store it in a graph store. Subsequently, it recalls knowledge relevant to your question by searching for triplets in the graph store.
Install Dependencies�
First, you need to install the dbgpt library.
uv sync --all-packages --frozen \
--extra "proxy_openai" \
--extra "rag" \
--extra "storage_chromadb" \
--extra "dbgpts"
--extra "graph_rag"
Prepare Graph Database
To store the knowledge in graph, we need an graph database, TuGraph is the first graph database supported by DB-GPT.
Visit github repository of TuGraph to view Quick Start document, follow the instructions to pull the TuGraph database docker image (latest / version >= 4.5.1) and launch it.
docker pull tugraph/tugraph-runtime-centos7:4.5.1
docker run -d -p 7070:7070 -p 7687:7687 -p 9090:9090 --name tugraph_demo tugraph/tugraph-runtime-centos7:latest lgraph_server -d run --enable_plugin true
The default port for the bolt protocol is 7687.
Download Tips:
There is also a corresponding version of the TuGraph Docker image package on OSS. You can also directly download and import it.
wget 'https://tugraph-web.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/tugraph/tugraph-4.5.1/tugraph-runtime-centos7-4.5.1.tar' -O tugraph-runtime-centos7-4.5.1.tar
docker load -i tugraph-runtime-centos7-4.5.1.tar
Prepare LLM
To build a Graph RAG program, we need a LLM, here are some of the LLMs that DB-GPT supports:
- Open AI(API)
- YI(API)
- API Server(cluster)
Then set your API key in the environment OPENAI_API_KEY.
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient()
You should have a YI account and get the API key from the YI official website.
Then set your API key in the environment variable YI_API_KEY.
If you have deployed DB-GPT cluster and API server , you can connect to the API server to get the LLM model.
The API is compatible with the OpenAI API, so you can use the OpenAILLMClient to connect to the API server.
First you should install the openai library.
pip install openai
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient(api_base="http://localhost:8100/api/v1/", api_key="{your_api_key}")
TuGraph Configuration
Set variables below in .env file, let DB-GPT know how to connect to TuGraph.
GRAPH_STORE_TYPE=TuGraph
TUGRAPH_HOST=127.0.0.1
TUGRAPH_PORT=7687
TUGRAPH_USERNAME=admin
TUGRAPH_PASSWORD=73@TuGraph
GRAPH_COMMUNITY_SUMMARY_ENABLED=True # enable the graph community summary
TRIPLET_GRAPH_ENABLED=True # enable the graph search for the triplets
DOCUMENT_GRAPH_ENABLED=True # enable the graph search for documents and chunks
KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_CHUNK_SEARCH_TOP_SIZE=5 # the number of the searched triplets in a retrieval
KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_EXTRACTION_BATCH_SIZE=20 # the batch size of triplet extraction from the text
COMMUNITY_SUMMARY_BATCH_SIZE=20 # the batch size of parallel community summary process
Load into Knowledge Graph
When using a graph database as the underlying knowledge storage platform, it is necessary to build a knowledge graph to facilitate the archiving and retrieval of documents. DB-GPT leverages the capabilities of large language models to implement an integrated knowledge graph, while still maintaining the flexibility to freely connect to other knowledge graph systems and graph database systems.
We created a knowledge graph with graph community summaries based on CommunitySummaryKnowledgeGraph.
from dbgpt.model.proxy.llms.chatgpt import OpenAILLMClient
from dbgpt.storage.knowledge_graph.community_summary import (
CommunitySummaryKnowledgeGraph,
CommunitySummaryKnowledgeGraphConfig,
)
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient()
model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"
def __create_community_kg_connector():
"""Create community knowledge graph connector."""
return CommunitySummaryKnowledgeGraph(
config=CommunitySummaryKnowledgeGraphConfig(
name="community_graph_rag_test",
embedding_fn=DefaultEmbeddingFactory.openai(),
llm_client=llm_client,
model_name=model_name,
graph_store_type="TuGraphGraph",
),
)
Retrieve from Knowledge Graph
Then you can retrieve the knowledge from the knowledge graph, which is the same with vector store.
import os
from dbgpt.configs.model_config import ROOT_PATH
from dbgpt.core import Chunk, HumanPromptTemplate, ModelMessage, ModelRequest
from dbgpt_ext.rag import ChunkParameters
from dbgpt_ext.rag.assembler import EmbeddingAssembler
from dbgpt_ext.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeFactory
from dbgpt.rag.retriever import RetrieverStrategy
async def test_community_graph_rag():
await __run_graph_rag(
knowledge_file="examples/test_files/graphrag-mini.md",
chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_MARKDOWN_HEADER",
knowledge_graph=__create_community_kg_connector(),
question="What's the relationship between TuGraph and DB-GPT ?",
)
async def __run_graph_rag(knowledge_file, chunk_strategy, knowledge_graph, question):
file_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, knowledge_file).format()
knowledge = KnowledgeFactory.from_file_path(file_path)
try:
chunk_parameters = ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy=chunk_strategy)
# get embedding assembler
assembler = await EmbeddingAssembler.aload_from_knowledge(
knowledge=knowledge,
chunk_parameters=chunk_parameters,
index_store=knowledge_graph,
retrieve_strategy=RetrieverStrategy.GRAPH,
)
await assembler.apersist()
# get embeddings retriever
retriever = assembler.as_retriever(1)
chunks = await retriever.aretrieve_with_scores(question, score_threshold=0.3)
# chat
print(f"{await ask_chunk(chunks[0], question)}")
finally:
knowledge_graph.delete_vector_name(knowledge_graph.get_config().name)
async def ask_chunk(chunk: Chunk, question) -> str:
rag_template = (
"Based on the following [Context] {context}, "
"answer [Question] {question}."
)
template = HumanPromptTemplate.from_template(rag_template)
messages = template.format_messages(context=chunk.content, question=question)
model_messages = ModelMessage.from_base_messages(messages)
request = ModelRequest(model=model_name, messages=model_messages)
response = await llm_client.generate(request=request)
if not response.success:
code = str(response.error_code)
reason = response.text
raise Exception(f"request llm failed ({code}) {reason}")
return response.text
Chat Knowledge via GraphRAG
Note: The current test data is in Chinese.
Here we demonstrate how to achieve chat knowledge through Graph RAG on web page.
First, create a knowledge base using the Knowledge Graph type.
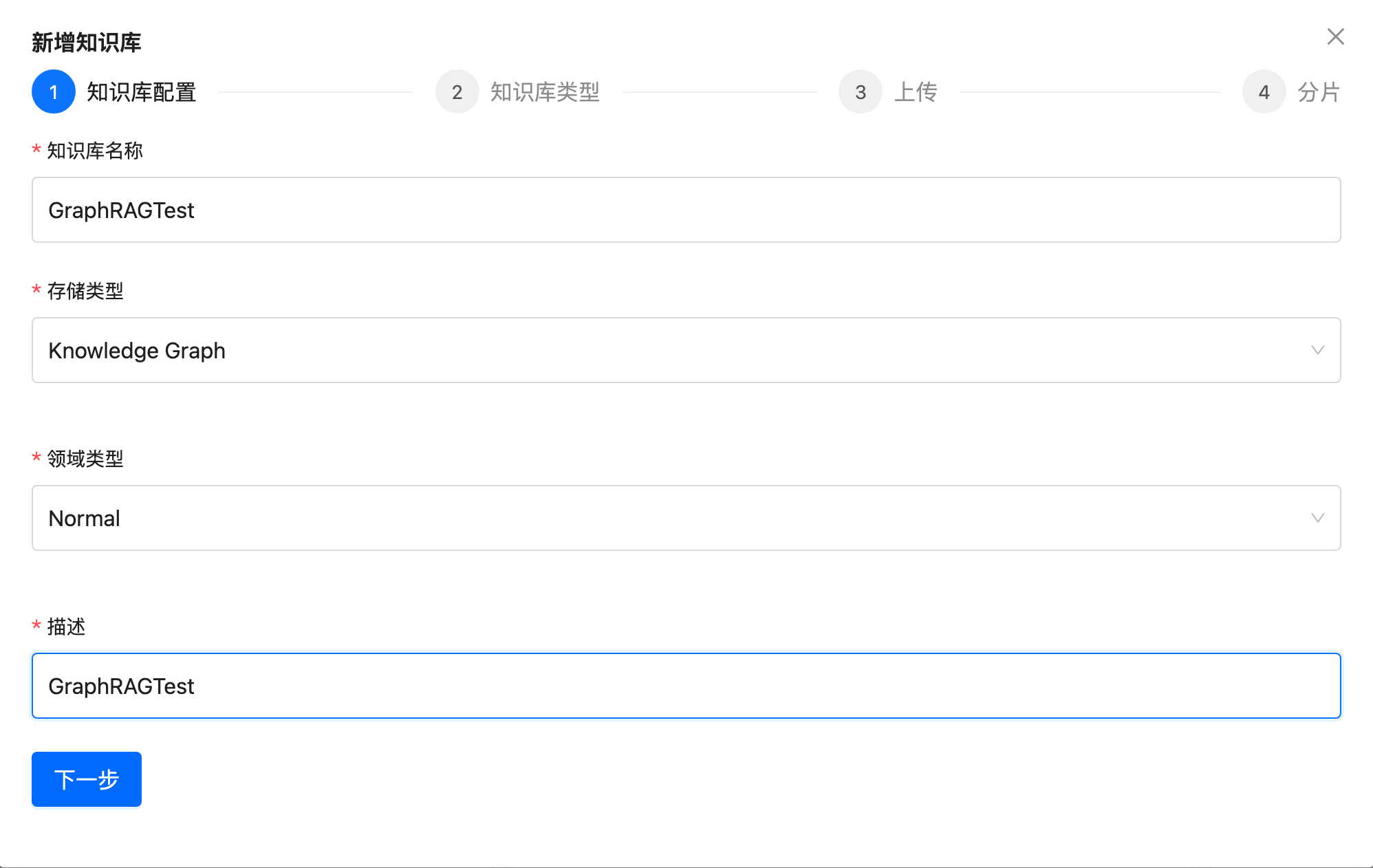
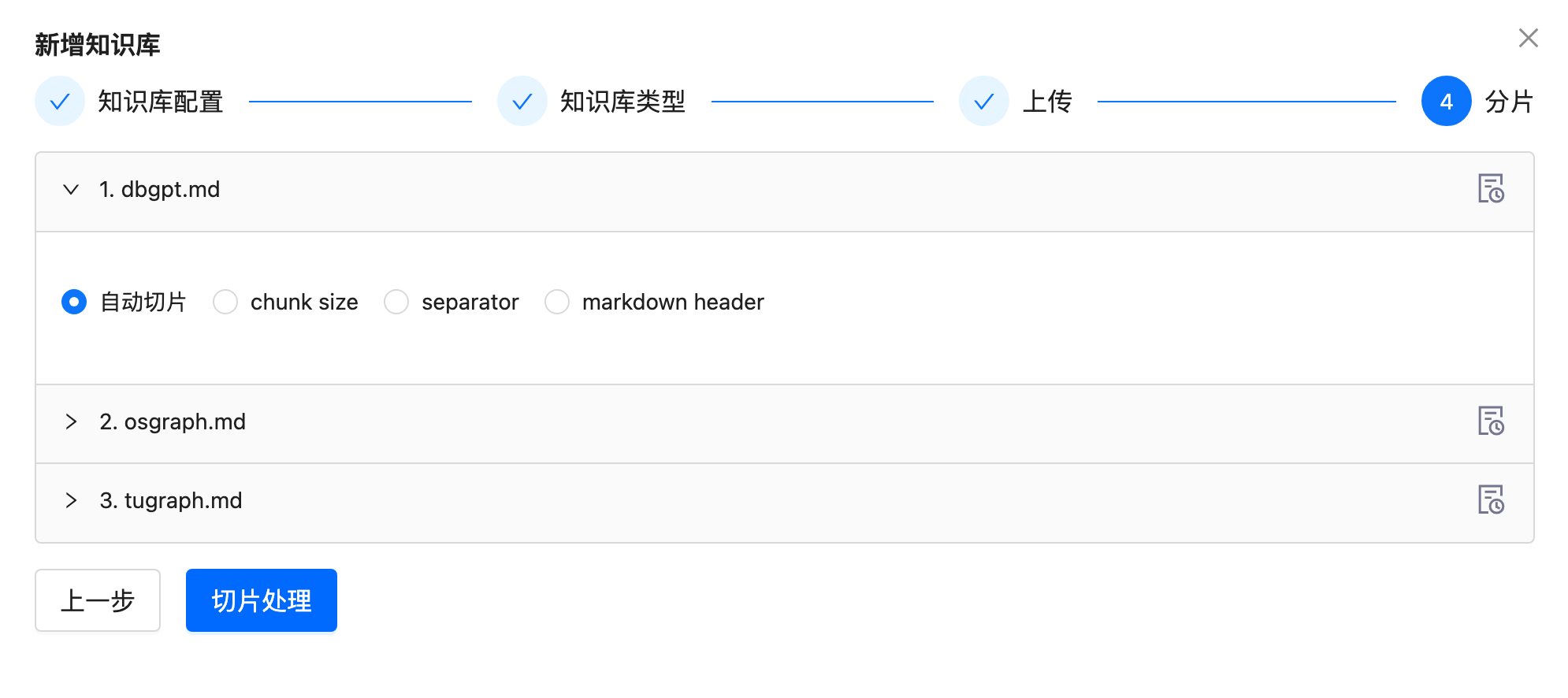
Then, upload the documents (graphrag-test.md) and process them automatically (markdown header by default).
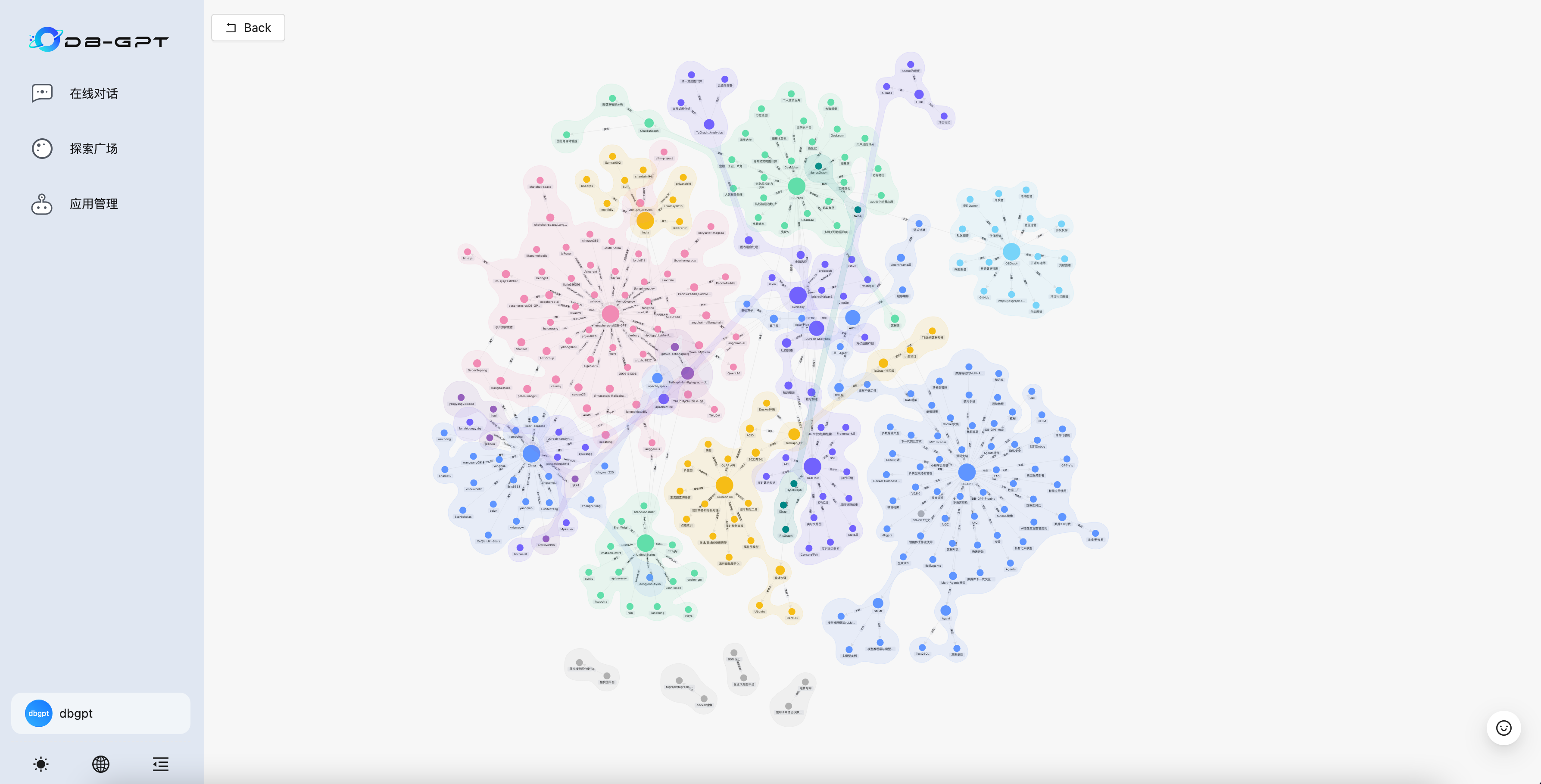
After indexing, the graph data may look like this.
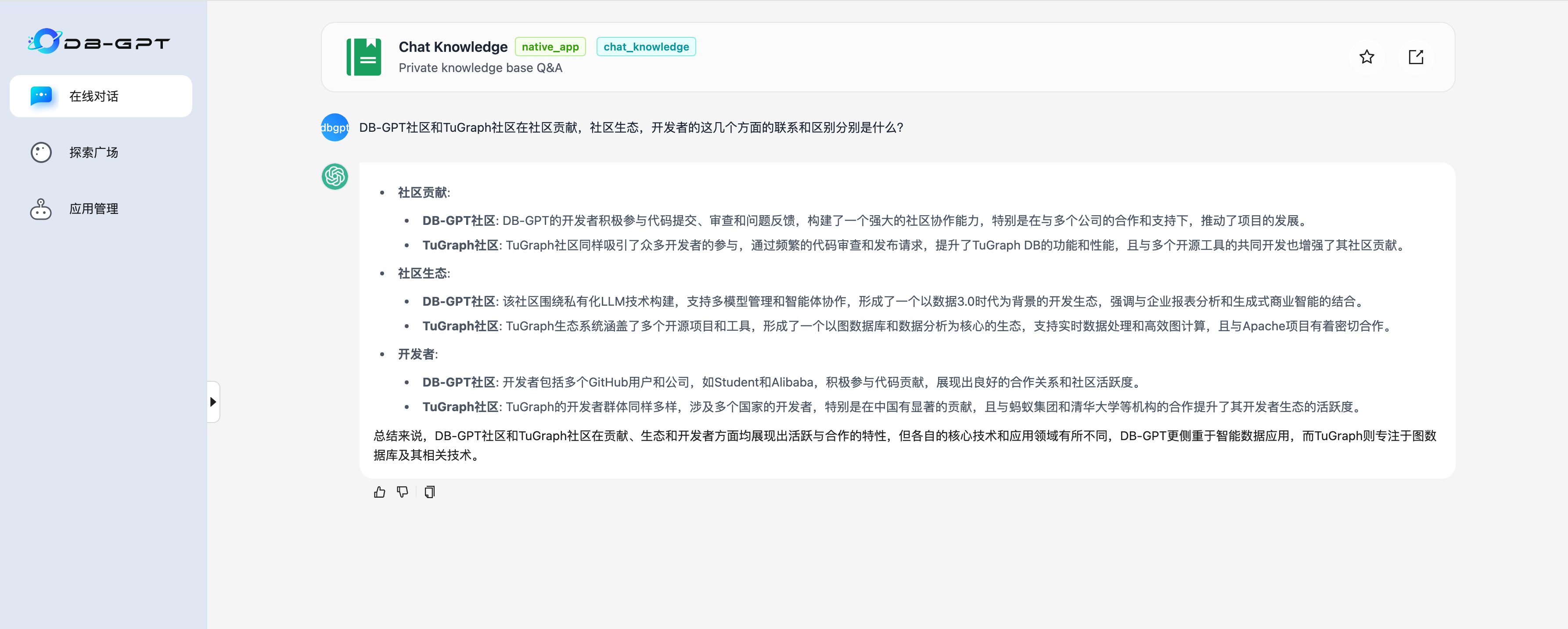
Start to chat on knowledge graph.
Performance Testing
Performance testing is based on the gpt-4o-mini model.
Indexing Performance
| DB-GPT | GraphRAG(microsoft) | |
|---|---|---|
| Doc Tokens | 42631 | 42631 |
| Triplets Graph | 734 nodes, 1064 edges | 779 nodes, 967 edges |
| Doc Structure Graph | 76 nodes, 1090 edges | N/A |
| Prompt Tokens | 375768 | 744990 |
| Completion Tokens | 41797 | 227230 |
| Total Tokens | 417565 | 972220 |
| Indexing Time | 170s | 210s |
Querying Performance
Global Search
| DB-GPT | GraphRAG(microsoft) | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | 8s | 40s |
| Tokens | 7432 | 63317 |
Question
请总结知识库的内容,并进行摘要说明。
- DB-GPT Answer
· 知识图谱概述: 知识图谱集中展示了与图数据库及相关处理系统的多种实体和其相互关联,涵盖了分布式内存图数据库、图计算模型及多种图处理框架和技术,强调了这些技术在图处理· 领域中的应用和相互影响。
· TuGraph DB: TuGraph DB是一种高效的图数据库,支持大数据容量和低延迟查找,具备ACID特性。其社区版适用于学习和小型项目,支持实时数据管理和多图结构。
· DB-GPT: DB-GPT是一个私有化的LLM技术数据库交互方式,支持多种高级功能,旨在推动数据3.0时代的到来。它提供了多模型管理、信息检索优化和智能体协作等功能。
· 应用领域: 知识库中提到的图技术应用于金融风控、社交网络和数据分析等多个领域,展示了图数据库的快速发展及其在各行各业中的重要性。
· 开发者生态: 知识库还强调了开发者在开源项目中的活跃表现,尤其是在Apache Flink和Spark等项目中的贡献,表明了良好的合作与开发生态。
整体而言,知识库展示了图数据库及其相关技术的广泛应用和快速进步,强调了DB-GPT和TuGraph等工具在数据智能和处理中的重要角色。
- GraphRAG(microsoft) Answer
知识库内容总结
概述
知识库涵盖了与图处理相关的多个社区和框架,强调了这些实体在推动技术解决方案和协作努力中的重要性。主要关注的领域包括图处理、人工智能开发和开源贡献。
关键实体
1. 图处理框架:知识库中提到的多个重要框架,如 GraphChi、X-Stream、GraphQ、PowerLyra、Gemini 和 TuGraph,均在处理大规模图数据方面发挥了重要作用。这些框架的相互关联性表明了一个促进创新的协作环境。
2. 企业贡献:一些主要企业如 Ant Group、Google、Tencent 和 Alibaba 在图处理和数据管理技术的发展中扮演了关键角色。它�们的合作关系强调了在推动技术创新方面的伙伴关系的重要性。
3. 开源项目:Apache 软件基金会的多个开源项目(如 Apache Hudi、Iceberg、Pulsar 和 Kafka)展示了全球开发者的贡献,增强了数据管理和分析能力。
发展趋势
知识库还指出了动态图处理、人工智能驱动的数据库管理和自动化工具集成等新兴趋势,这些趋势对于提高现代软件开发的效率和有效性至关重要。
结论
整体而言,知识库展示了一个充满活力的技术生态系统,其中各个实体通过合作和创新共同推动图处理和相关技术的发展。这种相互联系的网络不仅促进了技术的进步,也为解决复杂的技术挑战提供了支持。
Local Search
| DB-GPT | GraphRAG(microsoft) | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | 15s | 15s |
| Tokens | 9230 | 11619 |
Question
DB-GPT社区和TuGraph社区在社区贡献,社区生态,开发者的这几个方面的联系和区别分别是什么?
- DB-GPT Answer
· 社区贡献:
· DB-GPT社区: 由多个开发者和公司支持,开发者积极参与代码提交、审查和问题反馈,展现出强大的社区协作能力。主要合作项目包括Langchain-Chatchat、LLaMA-Factory、FastChat等。
· TuGraph社区: 吸引了众多开发者参与,专注于提升TuGraph DB的功能和性能,与多个开源工具共同开发,形成了活跃的贡献模式。
· 社区生态:
· DB-GPT社区: 主要围绕私有化LLM技术数据库交互方式,支持多种高级功能,促进数据智能应用开发,构建了一个以AI和数据处理为核心的生态。
· TuGraph社区: 依托于图数据库领域,尤其是TuGraph DB和TuGraph Analytics,形成了以大数据处理和实时计算为核心的生态,涉及多个行业应用,如金融风控和社交网络。
· 开发者:
· DB-GPT社区: 包含多个GitHub用户,开发者主要集中在AI和数据处理领域,积极参与开源项目的开发和维护。
· TuGraph社区: 涉及来自不同国家的开发者,特别是在图数据库和大数据分析领域的专业人员,强调多领域协作与贡献。
总体来看,DB-GPT社区和TuGraph社区在贡献方式和生态领域有所不同,前者更侧重于AI和数据交互技术,后者则专注于图数据库技术及其应用。
- GraphRAG(microsoft) Answer
DB-GPT社区与TuGraph社区的比较
DB-GPT社区和TuGraph社区在多个方面展现了各自的特点和贡献,尤其是在社区贡献、生态系统和开发者参与等方面。以下是对这两个社区的联系与区别的详细分析。
社区贡献
DB-GPT社区
DB-GPT社区围绕DB-GPT框架展开,整合了多个组织和资源,致力于AI和数据驱动应用的开发。该社区的主要贡献者包括Hiyouga、LM-Sys和Langchain-AI等组织,这些组织通过合作推动AI模型和应用的发展。DB-GPT的开发者们积极参与知识共享和技术创新,推动了AI应用的多样化和实用性。
TuGraph社区
TuGraph社区则专注于图数据库的开发,尤其是TuGraph及其相关项目。该社区的贡献者包括Ant Group和Tsinghua University等,致力于提供高效的图数据管理和分析解决方案。TuGraph社区的开发者们通过开源项目和技术文档,促进了图数据库技术的普及和应用。
社区生态
DB-GPT社区
DB-GPT社区的生态系统是一个多元化的合作网络,涵盖了多个组织和技术平台。该社区通过整合不同的技术和数据源,支持从聊天系统到企业报告等多种应用,展现出其在AI领域的广泛适用性。DB-GPT的生态系统强调了组织间的协作与知识共享,促进了技术的快速发展。
TuGraph社区
相较之下,TuGraph社区的生态系统更为专注于图数据的管理和分析。TuGraph及其相关项目(如TuGraph DB和TuGraph Analytics)共同构成了一个完整的图技术体系,支持大规模数据的实时处理和复杂分析。该社区的生态系统强调了图数据库在金融、工业和政务服务等领域的应用,展现了其在特定行业中的深度影响。
开发者参与
DB-GPT社区
在DB-GPT社区中,开发者的参与主要体现在对AI应用的开发和优化上。社区内的开发者通过贡献代码、参与讨论和解决问题,推动了DB-GPT框架的不断完善。该社区的开发者们来自�不同国家和地区,展现了全球范围内对AI技术的关注和参与。
TuGraph社区
TuGraph社区的开发者则主要集中在图数据库的构建和优化上。该社区的开发者们通过GitHub等平台积极参与项目的开发、代码审查和问题解决,推动了TuGraph技术的进步。TuGraph社区的开发者们同样来自中国及其他国家,展现了对图数据管理技术的广泛兴趣。
总结
总体而言,DB-GPT社区和TuGraph社区在社区贡献、生态系统和开发者参与等方面各具特色。DB-GPT社区更侧重于AI应用的多样性和组织间的合作,而TuGraph社区则专注于图数据的高效管理和分析。两者的共同点在于都强调了开源和社区合作的重要性,推动了各自领域的技术进步和应用发展。
Retrieval Of Document Structure
In version 0.6.1 of DB-GPT, we have added a new feature:
- Retrieval of triplets with the retrieval of document structure
We have expanded the definition scope of 'Graph' in GraphRAG:
Knowledge Graph = Triplets Graph + Document Structure Graph
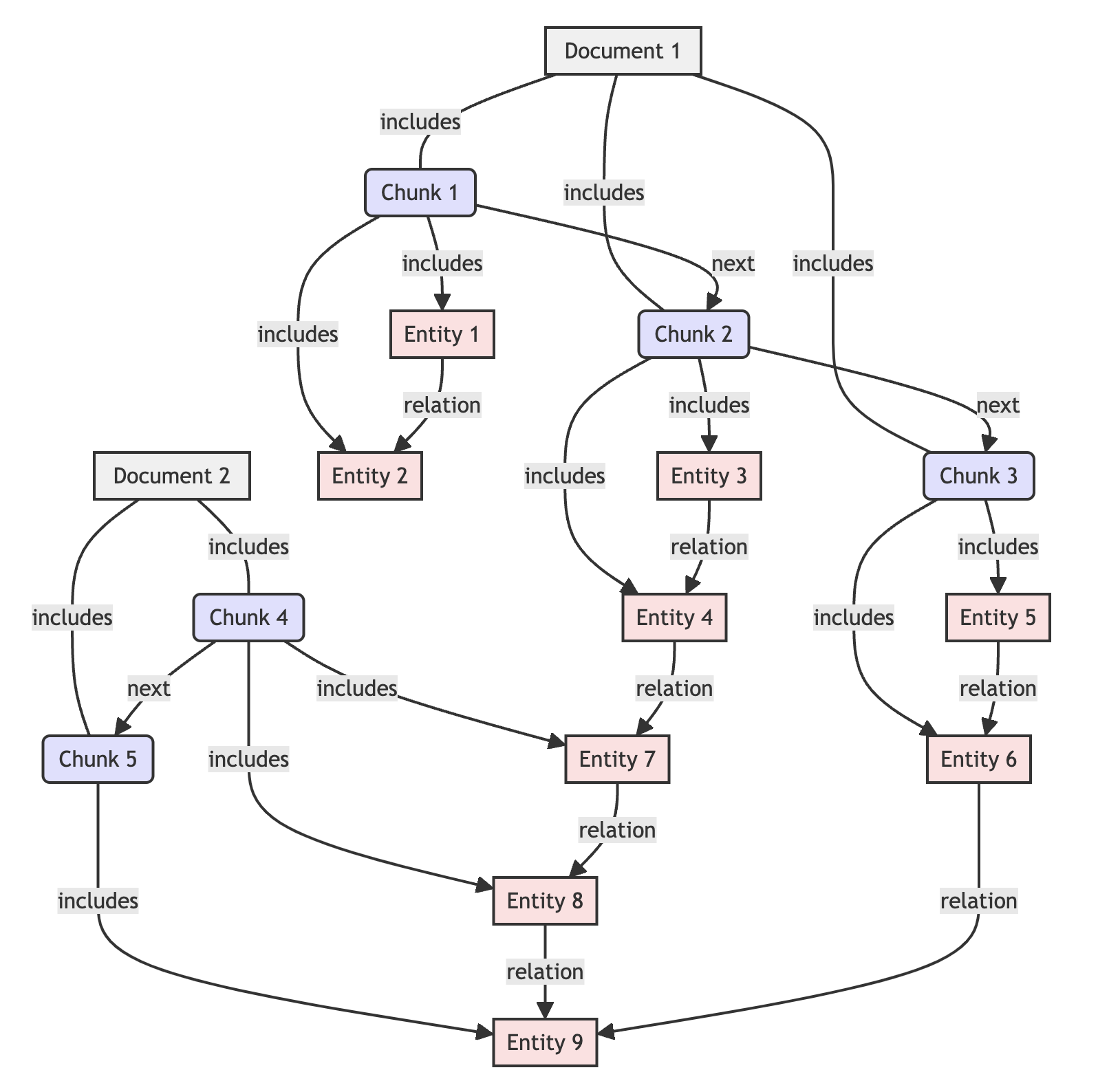
Thanks to the Document Structure Graph, GraphRAG now can provide references to the original text when answering:

How?
We decompose standard format files (currently best support for Markdown files) into a directed graph based on their hierarchy and layout information, and store it in a graph database. In this graph:
- Each node represents a chunk of the file
- Each edge represents the structural relationship between different chunks in the original document
- Merge the document structure graph to the triplets graph
What is the next?
We aim to construct a more complex Graph that covers more comprehensive information to support more sophisticated retrieval algorithms in our GraphRAG.
Similarity Search in GraphRAG:
In the latest version of DB-GPT, we have implemented a new feature:
- Similarity search for GraphRAG retrieval
How to use?
Use TuGraph 4.5.1 and above.
Set the variables below in the .env file to enable similarity search in DB-GPT.
SIMILARITY_SEARCH_ENABLED=True # enable the similarity search for entities and chunks
KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_EMBEDDING_BATCH_SIZE=20 # the batch size of embedding from the text
KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_SIMILARITY_SEARCH_TOP_SIZE=5 # set the topk of the vector similarity search
KNOWLEDGE_GRAPH_SIMILARITY_SEARCH_RECALL_SCORE=0.3 # set the reacall score of the vector similarity search
Additionally, you need to choose an embedding model in the .env file
## Openai embedding model, See dbgpt/model/parameter.py
# EMBEDDING_MODEL=proxy_openai
# proxy_openai_proxy_server_url=https://api.openai.com/v1
# proxy_openai_proxy_api_key={your-openai-sk}
# proxy_openai_proxy_backend=text-embedding-ada-002
## qwen embedding model, See dbgpt/model/parameter.py
# EMBEDDING_MODEL=proxy_tongyi
# proxy_tongyi_proxy_backend=text-embedding-v1
# proxy_tongyi_proxy_api_key={your-api-key}
## qianfan embedding model, See dbgpt/model/parameter.py
#EMBEDDING_MODEL=proxy_qianfan
#proxy_qianfan_proxy_backend=bge-large-zh
#proxy_qianfan_proxy_api_key={your-api-key}
#proxy_qianfan_proxy_api_secret={your-secret-key}
Why to use?
TuGraph now offers comprehensive vector capabilities, including vector storage, indexing, and similarity search functionalities. These features enable GraphRAG to achieve superior retrieval performance compared to traditional keyword-based approaches.
To leverage these capabilities, we've introduced an _embedding field in both entity and chunk objects to store embedding data, enabling similarity search to identify the most relevant results for a given query.
Comparison of Similarity Search Results
Given identical documents and questions in the same environment, the results of the keyword mode are as follows:

The results of the similarity search mode are as follows:
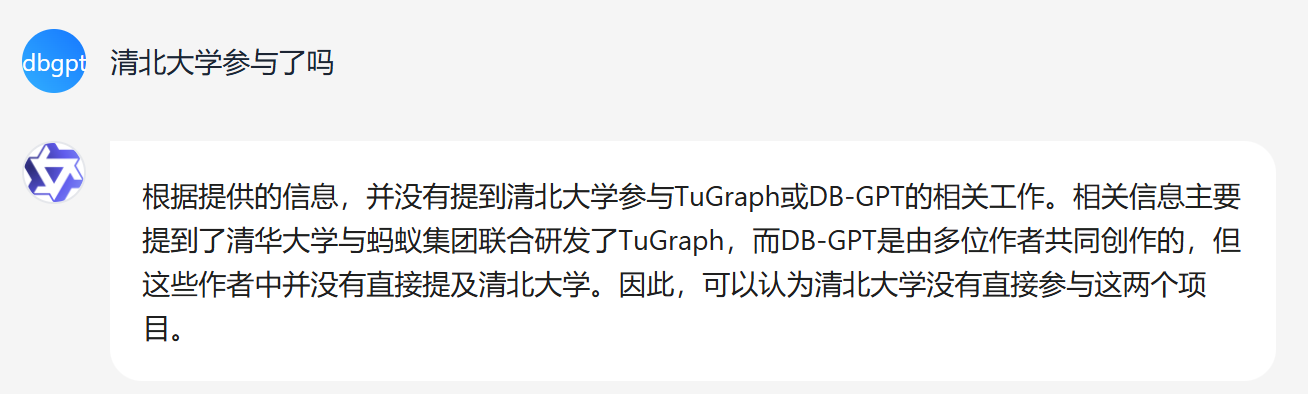
Compared to the keyword search method, the similarity search method can cover more comprehensive information. For instance, when dealing with the term 清北大学 in the keyword search mode, it is hard to extract useful keywords. However, the similarity search mode can identify similar words, enabling it to retrieve relevant information related to Tsinghua University and thus include it in the search results.
This implies that in scenarios where queries are imprecise, the similarity search approach can retrieve more pertinent information compared to keyword-based search patterns.
Furthermore, as shown in the following figure, compared to RAG, GraphRAG with similarity search can obtain more relevant information, ensuring richer answers.
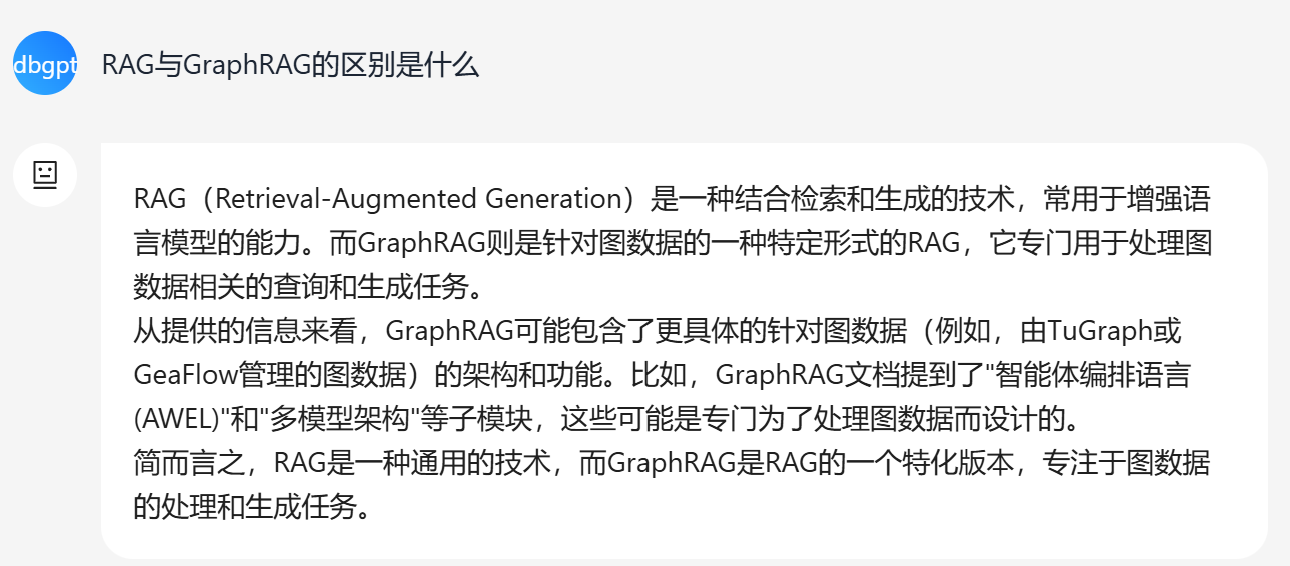
In conclusion, enabling similarity search in GraphRAG significantly expands the scope and relevance of its responses.
Text2GQL Search in GraphRAG:
In the latest version of DB-GPT, we have implemented a new feature:
- Text2GQL search for GraphRAG retrieval
How to use?
Set the variables below in the .env file to enable text2gql search in DB-GPT.
TEXT2GQL_SEARCH_ENABLED=True # enable the text2gql search for entities and relations.
Why to use?
Keywords or vectors based retrieval will generate large multihop subgraph for LLM to summarize information, but this method is costive when questions asked by users can be simply expressed by a single graph query. Text2GQL search can effectively reduce the cost of graph search and increase the accuracy of the retrieved subgraph under above situation.
In the future, we hope to further improve the ability of Text2GQL translation to compete with keywords or vectors based retrieval under complicated questions with both prompt based method and finetune based method.
Comparison of Text2GQL Search Results
Given identical documents and questions in the same environment, the results of the keyword mode are as follows:

The results of the text2gql search mode are as follows:
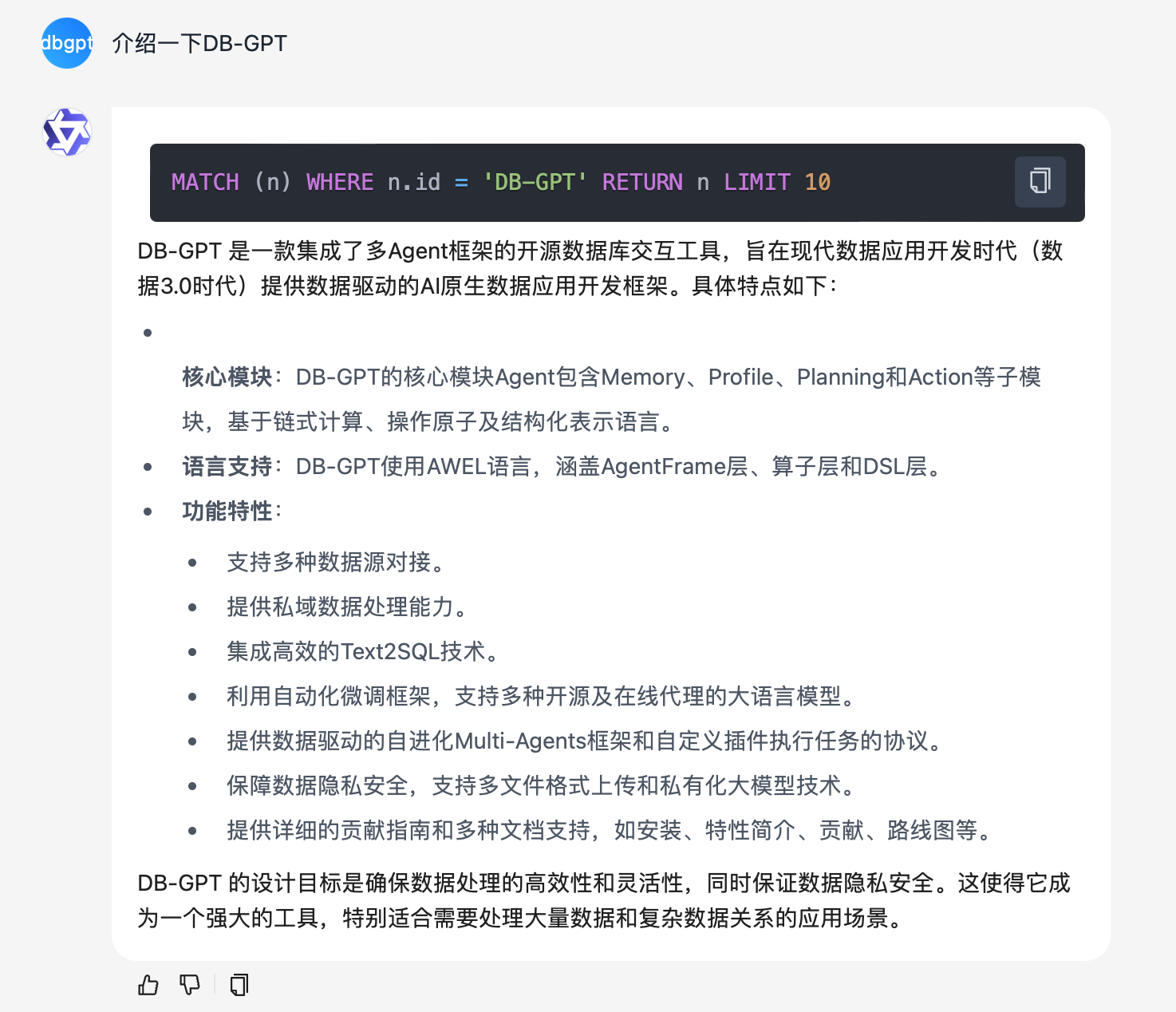
Compared to the keyword search method, the text2gql search method can generate an accurate graph query laguage to query the entity of DB-GPT in knowledge graph, which is
MATCH (n) WHERE n.id = 'DB-GPT' RETURN n LIMIT 10
This implies that in scenarios where questions can be expressed by a single graph query, the text2gql search approach can retrieve more accurate information with lower cost.
In conclusion, enabling text2gql search in GraphRAG significantly increase the accuracy and lower the cost when questions are concise and clear.