Keyword Search RAG User Manual
In this example, we will show how to use the Full Text Search RAG framework in DB-GPT. Using traditional full-text search to implement RAG can, to some extent, alleviate the uncertainty and interpretability issues brought about by vector database retrieval.
You can refer to the python example file DB-GPT/examples/rag/keyword_rag_example.py in the source code. This example demonstrates how to load knowledge from a document and persist it in a full text store. Subsequently, it recalls knowledge relevant to your question by searching for keywords in the full text store.
The Constraints of Vector Retrieve
Vector Retrieve offers clear advantages, the technology does have some constraints:
- Computationally Intensive - Generating vectors for entire corpora of documents and querying based on vector similarity requires significantly more processing power than keyword indexing and matching. Latency can be an issue if systems are not properly optimized.
- Requires Massive Training Data - The semantic connections made by models like BERT rely on being trained on massive, diverse datasets over long periods. This data may not be readily available for specialized corpora, limiting the quality of vectors.
- Less Effective for Precise Keyword Queries - Vector search adds little benefit when queries contain clear, precise keywords and intent. Searching for "apple fruit" would likely return poorer results than just "apple" because the vector focuses on overall meaning more than keywords.
How to choose Between Vector Retrieve and Keyword Retrieve ?
When is vector search preferable over keyword search, and vice versa? Here are some best practices on when to use each:
When to Use Vector Search
Early stage research when query intent is vague or broad Need to grasp concepts and subject matter more than keywords Exploring a topic with loose information needs User search queries are more conversational The semantic capabilities of vector search allow it to shine for these use cases. It can point users in the right direction even with limited keywords or understanding of a topic.
When to Use Keyword Search:
- Looking for something ultra-specific and already understand the topic
- Research is narrowly focused with clear objectives
- Queries contain unique proper nouns like brand names
- Needs require fast results more than exhaustive relevancy For precise or time-sensitive queries, keyword search will target the exact terms efficiently. Vector search may meander with unnecessary semantic expansion.
The search method should align with the user's intent and specificity needs. Vector search for exploration, keyword search for precision. With both available, users get the best of both worlds.
Install Dependencies
First, you need to install the dbgpt library.
pip install "dbgpt[rag]>=0.5.8"
Prepare Full Text Search Engine
Elasticsearch is the distributed search and analytics engine at the heart of the Elastic Stack. Logstash and Beats facilitate collecting, aggregating, and enriching your data and storing it in Elasticsearch. Kibana enables you to interactively explore, visualize, and share insights into your data and manage and monitor the stack. Elasticsearch is where the indexing, search, and analysis magic happens.
refer https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/elasticsearch-intro.html
Install Elasticsearch refer https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/install-elasticsearch.html
Keyword Search Configuration
Set variables below in .env file, let DB-GPT know how to connect to Full Text Search Engine Storage.
ELASTICSEARCH_URL=localhost
ELASTICSEARCH_PORT=9200
ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME=elastic
ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD=dbgpt
Load into Full Text Search Engine
When using a Elaticsearch full text engine as the underlying knowledge storage platform, it is necessary to build document inverted index to facilitate the archiving and retrieval of documents.
The following code demonstrates how to create a connection to the Elasticsearch search engine.
from dbgpt_ext.storage.full_text.elasticsearch import ElasticDocumentConfig, \
ElasticDocumentStore
def _create_es_connector():
"""Create es connector."""
config = ElasticDocumentConfig(
name="keyword_rag_test",
uri="localhost",
port="9200",
user="elastic",
password="dbgpt",
)
return ElasticDocumentStore(config)
Keyword Retrieve from Full Text Search Engine
Keyword Retrieve is a simple and efficient way to retrieve relevant information from a large number of documents. It is based on the full-text search engine Elasticsearch. The user can input a query and retrieve the most relevant documents based on the query.
import os
from dbgpt.configs.model_config import ROOT_PATH
from dbgpt_ext.rag import ChunkParameters
from dbgpt_ext.rag.assembler import EmbeddingAssembler
from dbgpt_ext.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeFactory
async def main():
file_path = os.path.join(ROOT_PATH, "docs/docs/awel/awel.md")
knowledge = KnowledgeFactory.from_file_path(file_path)
keyword_store = _create_es_connector()
chunk_parameters = ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_SIZE")
# get embedding assembler
assembler = EmbeddingAssembler.load_from_knowledge(
knowledge=knowledge,
chunk_parameters=chunk_parameters,
index_store=keyword_store,
)
assembler.persist()
# get embeddings retriever
retriever = assembler.as_retriever(3)
chunks = await retriever.aretrieve_with_scores("what is awel talk about", 0.3)
print(f"keyword rag example results:{chunks}")
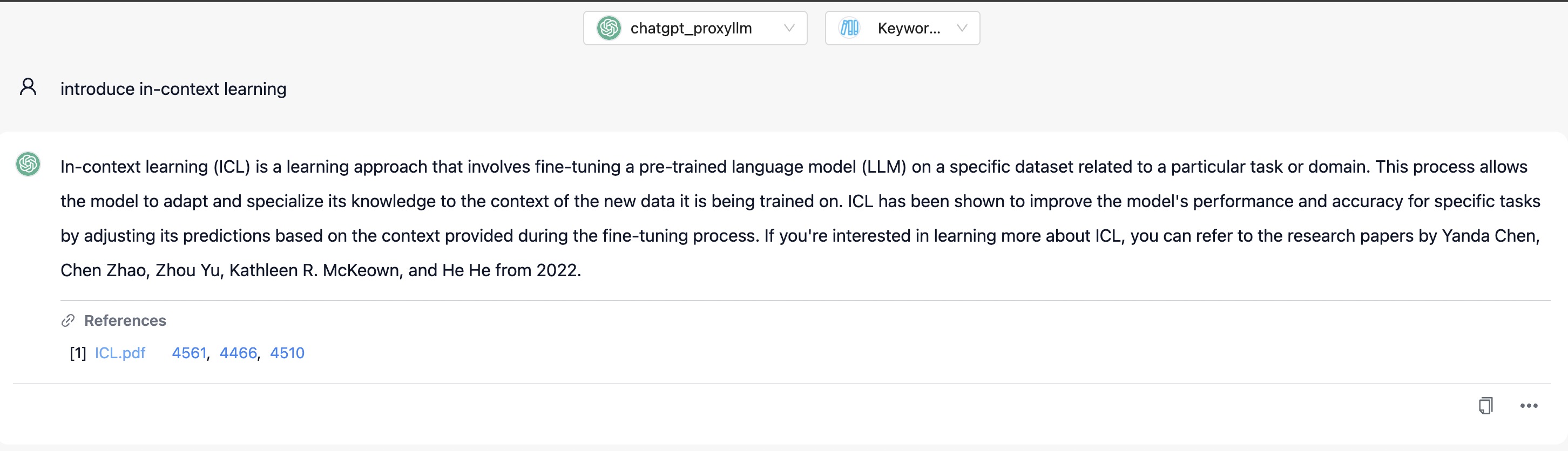
Chat Knowledge via Keyword RAG
Here we demonstrate how to achieve chat knowledge through Keyword RAG on web page.
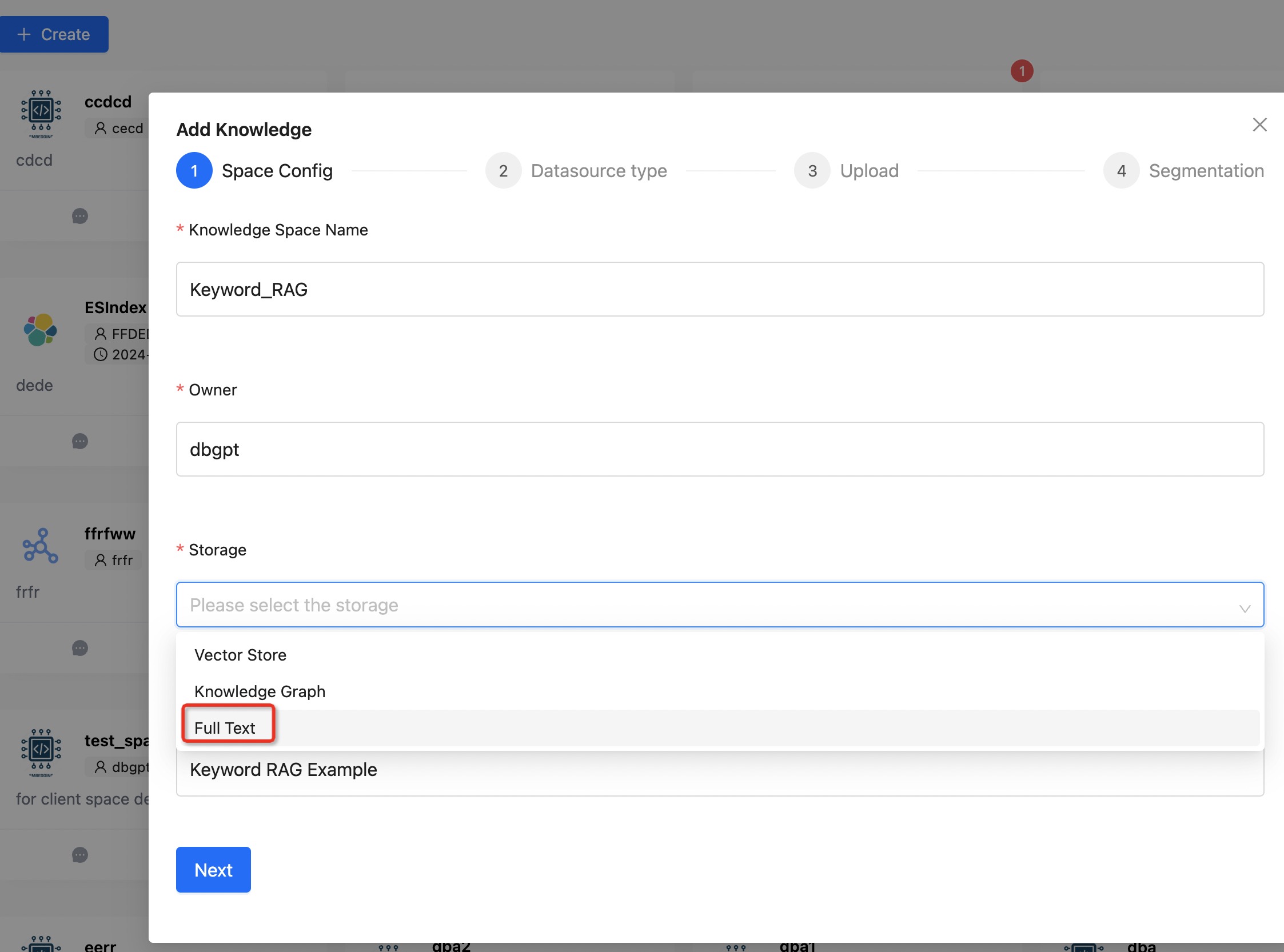
First, create a knowledge base using the Full Text type. Upload the knowledge documents and wait for the slicing to complete.
Start chat to knowledge based on Keyword RAG.