RAG With AWEL
In this example, we will show how to use the AWEL library to create a RAG program.
Now, let us create a python file first_rag_with_awel.py.
In this example, we will load your knowledge from a URL and store it in a vector store.
Install Dependencies
First, you need to install the dbgpt library.
pip install "dbgpt[rag]>=0.5.2"
Prepare Embedding Model
To store the knowledge in a vector store, we need an embedding model, DB-GPT supports a lot of embedding models, here are some of them:
- Open AI(API)
- text2vec(local)
- Embedding API Server(cluster)
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactory
embeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.openai()
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactory
embeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.default("/data/models/text2vec-large-chinese")
If you have deployed DB-GPT cluster and API server , you can connect to the API server to get the embeddings.
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactory
embeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.remote(
api_url="http://localhost:8100/api/v1/embeddings",
api_key="{your_api_key}",
model_name="text2vec"
)
Load Knowledge And Store In Vector Store
Then we can create a DAG which loads the knowledge from a URL and stores it in a vector store.
import asyncio
import shutil
from dbgpt.core.awel import DAG
from dbgpt.rag import ChunkParameters
from dbgpt.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeType
from dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingAssemblerOperator, KnowledgeOperator
from dbgpt.storage.vector_store.chroma_store import ChromaStore, ChromaVectorConfig
# Delete old vector store directory(/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store)
shutil.rmtree("/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store", ignore_errors=True)
vector_store = ChromaStore(
vector_store_config=ChromaVectorConfig(
name="test_vstore",
persist_path="/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store",
embedding_fn=embeddings
)
)
with DAG("load_knowledge_dag") as knowledge_dag:
# Load knowledge from URL
knowledge_task = KnowledgeOperator(knowledge_type=KnowledgeType.URL.name)
assembler_task = EmbeddingAssemblerOperator(
index_store=vector_store,
chunk_parameters=ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_SIZE")
)
knowledge_task >> assembler_task
chunks = asyncio.run(assembler_task.call("https://docs.dbgpt.site/docs/awel/"))
print(f"Chunk length: {len(chunks)}")
Retrieve Knowledge From Vector Store
Then you can retrieve the knowledge from the vector store.
from dbgpt.core.awel import MapOperator
from dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingRetrieverOperator
with DAG("retriever_dag") as retriever_dag:
retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(
top_k=3,
index_store=vector_store,
)
content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))
retriever_task >> content_task
chunks = asyncio.run(content_task.call("What is the AWEL?"))
print(chunks)
Prepare LLM
To build a RAG program, we need a LLM, here are some of the LLMs that DB-GPT supports:
- Open AI(API)
- YI(API)
- API Server(cluster)
First, you should install the openai library.
pip install openai
Then set your API key in the environment OPENAI_API_KEY.
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient()
You should have a YI account and get the API key from the YI official website.
First, you should install the openai library.
pip install openai
Then set your API key in the environment variable YI_API_KEY.
from dbgpt.model.proxy import YiLLMClient
llm_client = YiLLMClient()
If you have deployed DB-GPT cluster and API server , you can connect to the API server to get the LLM model.
The API is compatible with the OpenAI API, so you can use the OpenAILLMClient to connect to the API server.
First you should install the openai library.
pip install openai
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient(api_base="http://localhost:8100/api/v1/", api_key="{your_api_key}")
Create RAG Program
Lastly, we can create a RAG with the retrieved knowledge.
from dbgpt.core.awel import InputOperator, JoinOperator, InputSource
from dbgpt.core.operators import PromptBuilderOperator, RequestBuilderOperator
from dbgpt.model.operators import LLMOperator
prompt = """Based on the known information below, provide users with professional and concise answers to their questions.
If the answer cannot be obtained from the provided content, please say:
"The information provided in the knowledge base is not sufficient to answer this question.".
It is forbidden to make up information randomly. When answering, it is best to summarize according to points 1.2.3.
known information:
{context}
question:
{question}
"""
with DAG("llm_rag_dag") as rag_dag:
input_task = InputOperator(input_source=InputSource.from_callable())
retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(
top_k=3,
index_store=vector_store,
)
content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))
merge_task = JoinOperator(lambda context, question: {"context": context, "question": question})
prompt_task = PromptBuilderOperator(prompt)
# The model is gpt-3.5-turbo, you can replace it with other models.
req_build_task = RequestBuilderOperator(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
llm_task = LLMOperator(llm_client=llm_client)
result_task = MapOperator(lambda r: r.text)
input_task >> retriever_task >> content_task >> merge_task
input_task >> merge_task
merge_task >> prompt_task >> req_build_task >> llm_task >> result_task
print(asyncio.run(result_task.call("What is the AWEL?")))
The output will be:
AWEL stands for Agentic Workflow Expression Language, which is a set of intelligent agent workflow expression language designed for large model application development. It simplifies the process by providing functionality and flexibility through its layered API design architecture, including the operator layer, AgentFrame layer, and DSL layer. Its goal is to allow developers to focus on business logic for LLMs applications without having to deal with intricate model and environment details.
Congratulations! You have created a RAG program with AWEL.
Full Code
And let's look the full code of first_rag_with_awel.py:
import asyncio
import shutil
from dbgpt.core.awel import DAG, MapOperator, InputOperator, JoinOperator, InputSource
from dbgpt.core.operators import PromptBuilderOperator, RequestBuilderOperator
from dbgpt.rag import ChunkParameters
from dbgpt.rag.knowledge import KnowledgeType
from dbgpt.rag.operators import EmbeddingAssemblerOperator, KnowledgeOperator,
EmbeddingRetrieverOperator
from dbgpt.rag.embedding import DefaultEmbeddingFactory
from dbgpt.storage.vector_store.chroma_store import ChromaStore, ChromaVectorConfig
from dbgpt.model.operators import LLMOperator
from dbgpt.model.proxy import OpenAILLMClient
# Here we use the openai embedding model, if you want to use other models, you can
# replace it according to the previous example.
embeddings = DefaultEmbeddingFactory.openai()
# Here we use the openai LLM model, if you want to use other models, you can replace
# it according to the previous example.
llm_client = OpenAILLMClient()
# Delete old vector store directory(/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store)
shutil.rmtree("/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store", ignore_errors=True)
vector_store = ChromaStore(
vector_store_config=ChromaVectorConfig(
name="test_vstore",
persist_path="/tmp/awel_rag_test_vector_store",
embedding_fn=embeddings
),
)
with DAG("load_knowledge_dag") as knowledge_dag:
# Load knowledge from URL
knowledge_task = KnowledgeOperator(knowledge_type=KnowledgeType.URL.name)
assembler_task = EmbeddingAssemblerOperator(
index_store=vector_store,
chunk_parameters=ChunkParameters(chunk_strategy="CHUNK_BY_SIZE")
)
knowledge_task >> assembler_task
chunks = asyncio.run(assembler_task.call("https://docs.dbgpt.site/docs/awel/"))
print(f"Chunk length: {len(chunks)}\n")
prompt = """Based on the known information below, provide users with professional and concise answers to their questions.
If the answer cannot be obtained from the provided content, please say:
"The information provided in the knowledge base is not sufficient to answer this question.".
It is forbidden to make up information randomly. When answering, it is best to summarize according to points 1.2.3.
known information:
{context}
question:
{question}
"""
with DAG("llm_rag_dag") as rag_dag:
input_task = InputOperator(input_source=InputSource.from_callable())
retriever_task = EmbeddingRetrieverOperator(
top_k=3,
index_store=vector_store,
)
content_task = MapOperator(lambda cks: "\n".join(c.content for c in cks))
merge_task = JoinOperator(
lambda context, question: {"context": context, "question": question})
prompt_task = PromptBuilderOperator(prompt)
# The model is gpt-3.5-turbo, you can replace it with other models.
req_build_task = RequestBuilderOperator(model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
llm_task = LLMOperator(llm_client=llm_client)
result_task = MapOperator(lambda r: r.text)
input_task >> retriever_task >> content_task >> merge_task
input_task >> merge_task
merge_task >> prompt_task >> req_build_task >> llm_task >> result_task
print(asyncio.run(result_task.call("What is the AWEL?")))
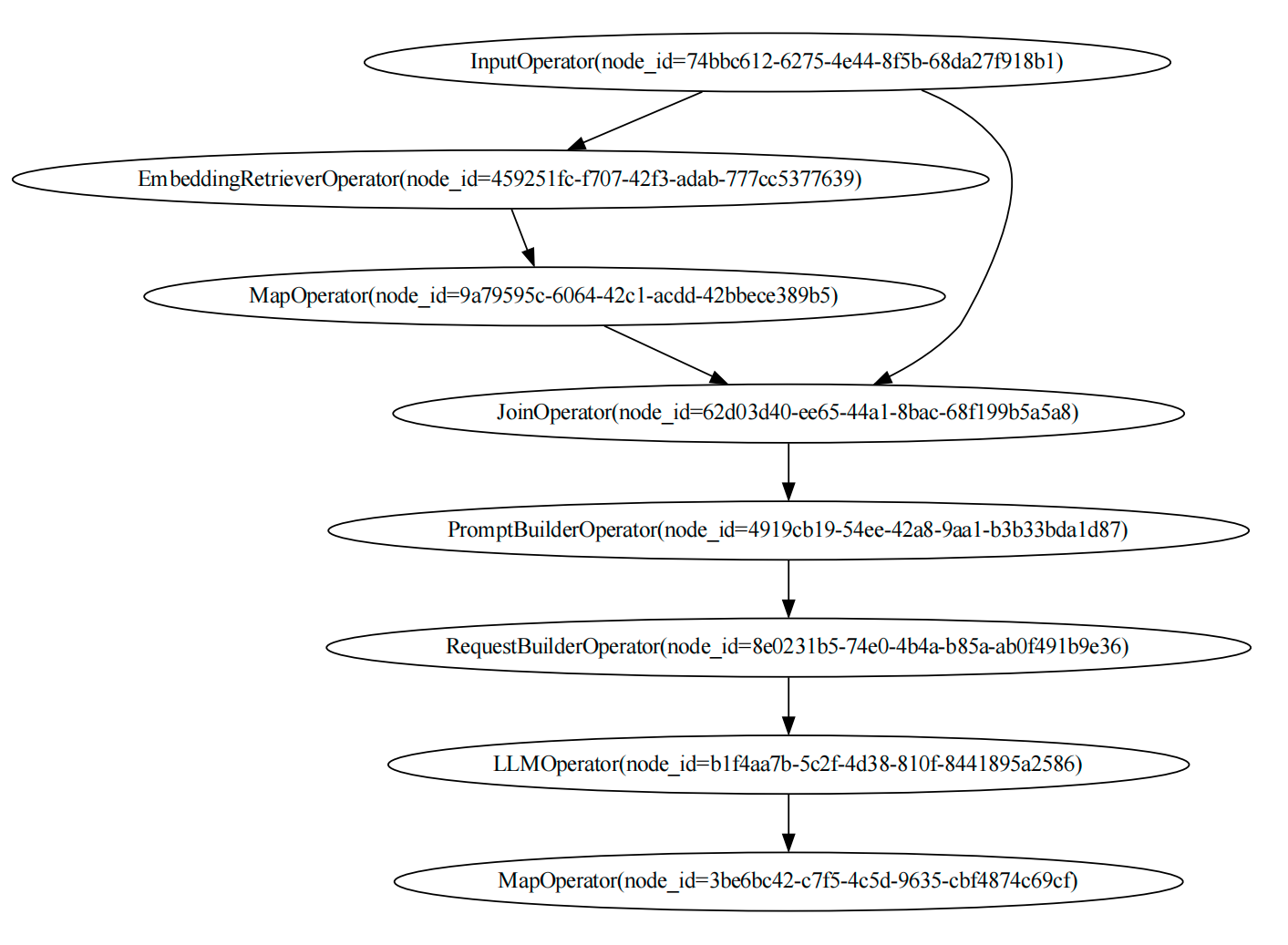
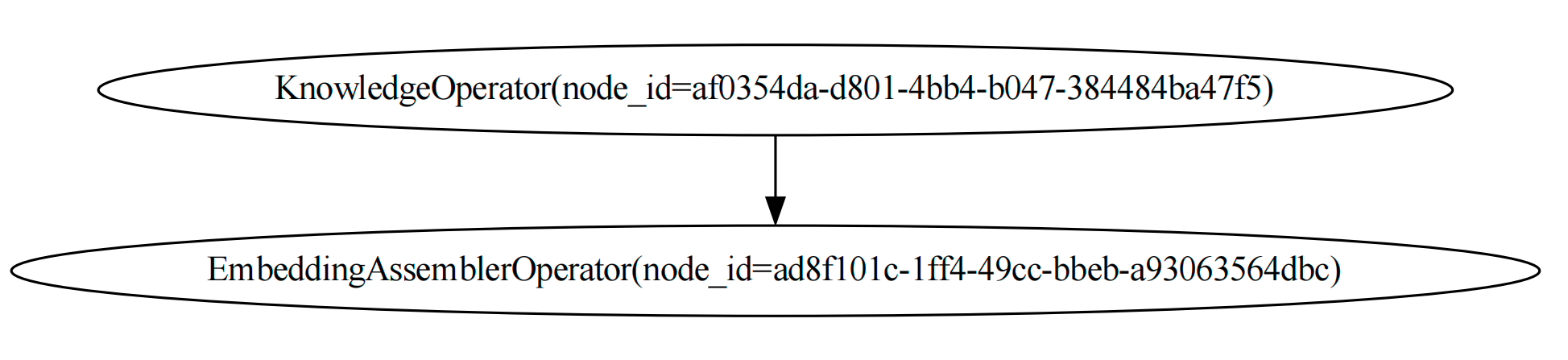
Visualize DAGs
And we can visualize the DAGs with the following code:
knowledge_dag.visualize_dag()
rag_dag.visualize_dag()
If you execute the code in Jupyter Notebook, you can see the DAGs in the notebook.
display(knowledge_dag.show())
display(rag_dag.show())
The graph of the knowledge_dag is:
And the graph of the rag_dag is: