SMMF
The DB-GPT project provides service-oriented multi-model management capabilities. Developer who are interested in related capabilities can read the SMMF module part. Here we focus on how to use multi-LLMs.
Here we mainly introduce the usage through the web interface. For developer interested in the command line, you can refer to the cluster deployment model. Open the DB-GPT-Web frontend service and click on Model Management to enter the multi-model management interface.
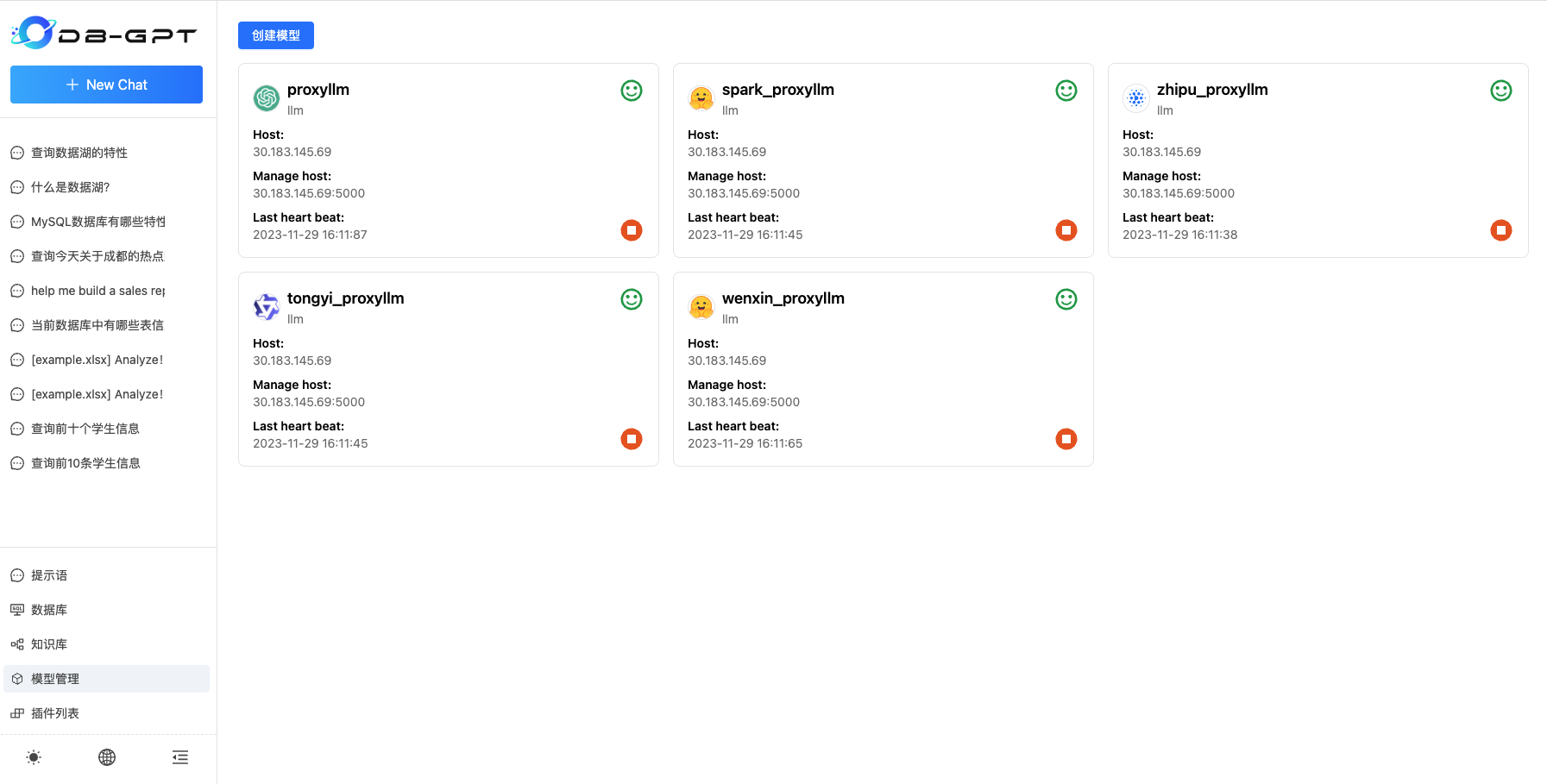
List Models
By opening the model management interface, we can see the list of currently deployed models. The following is the list of models.
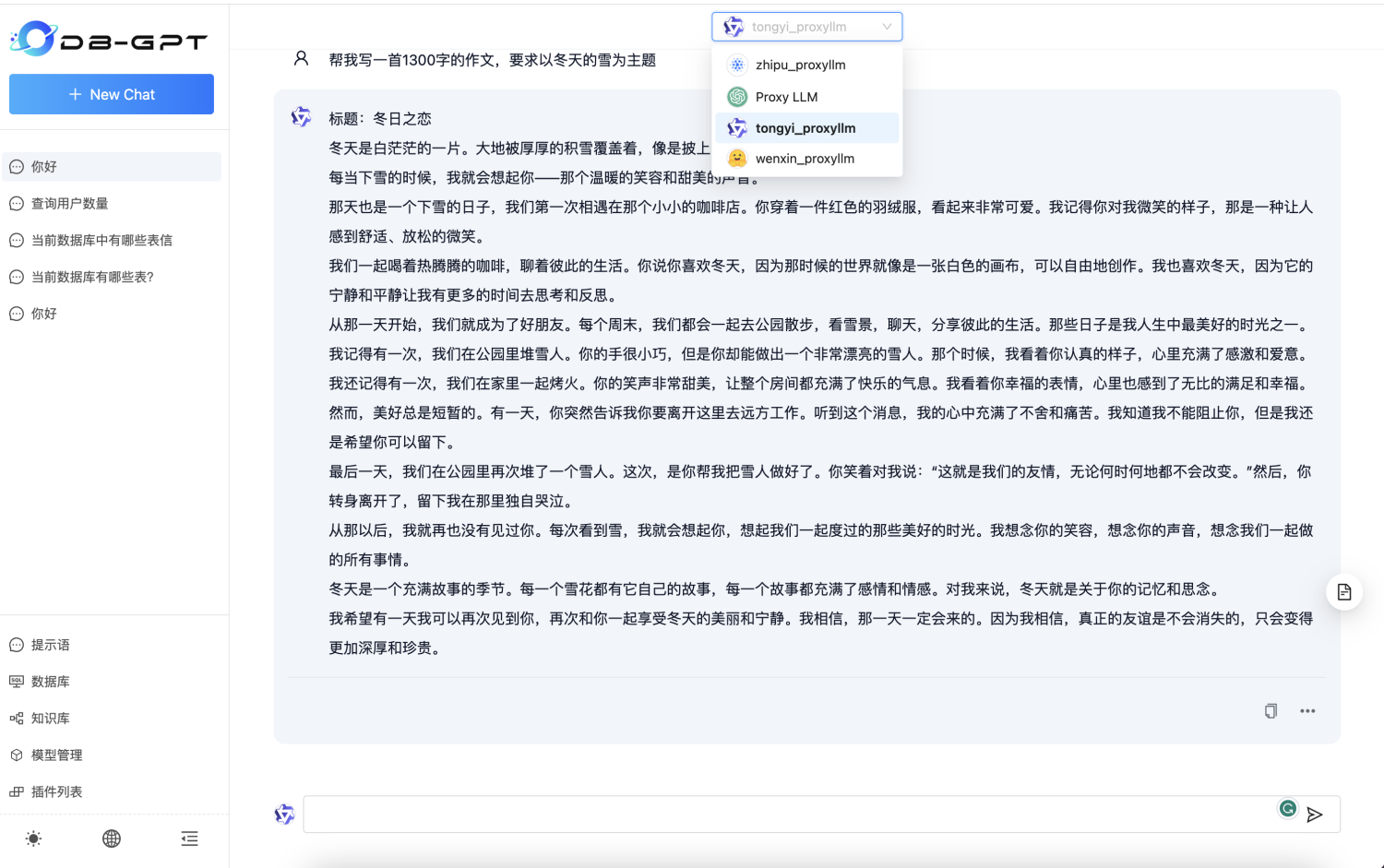
Use Models
Once the models are deployed, you can switch and use the corresponding model on the multi-model interface.
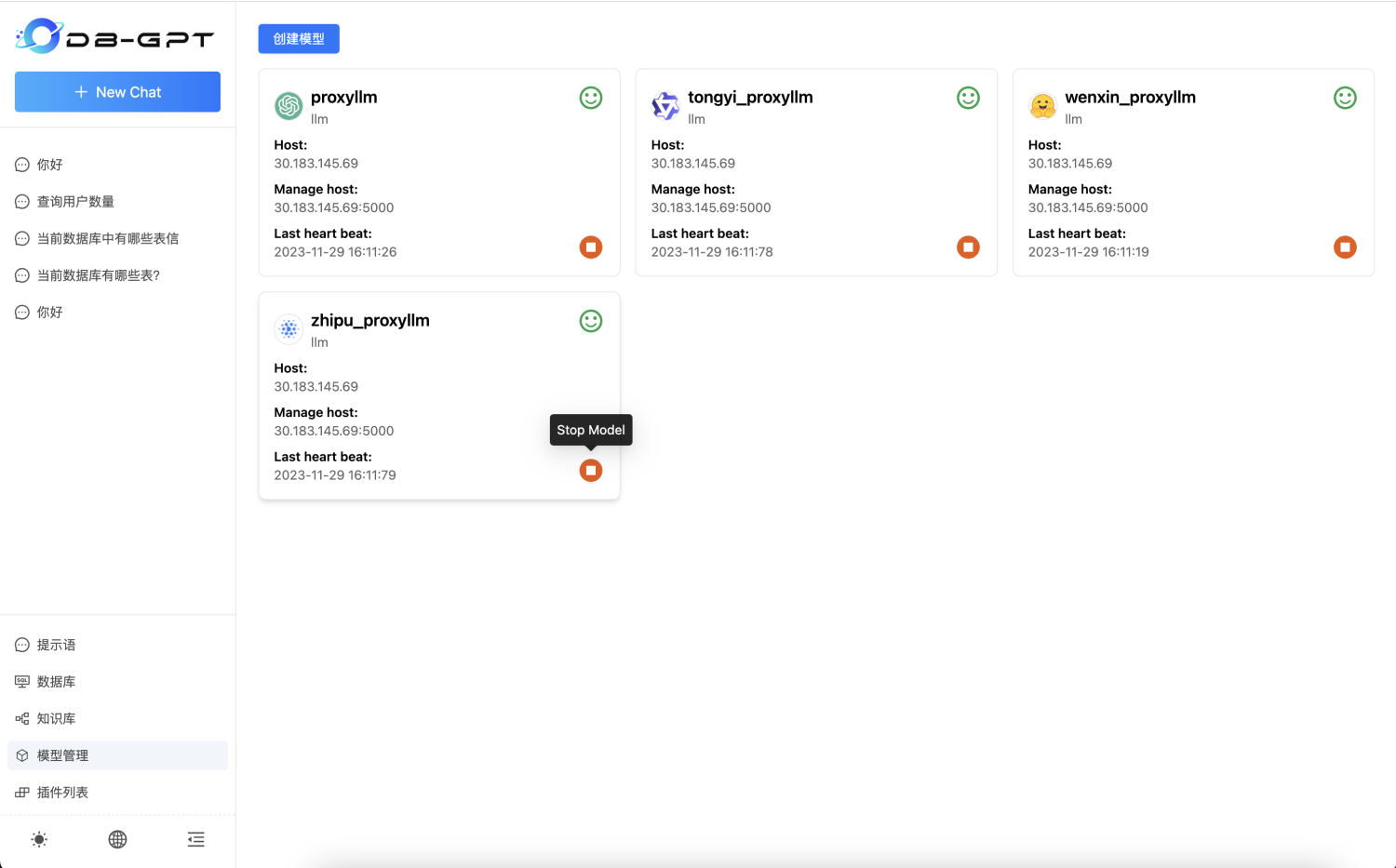
Stop Models
As shown in the figure below, click Model Management to enter the model list interface. Select a specific model and click the red Stop Model button to stop the model.
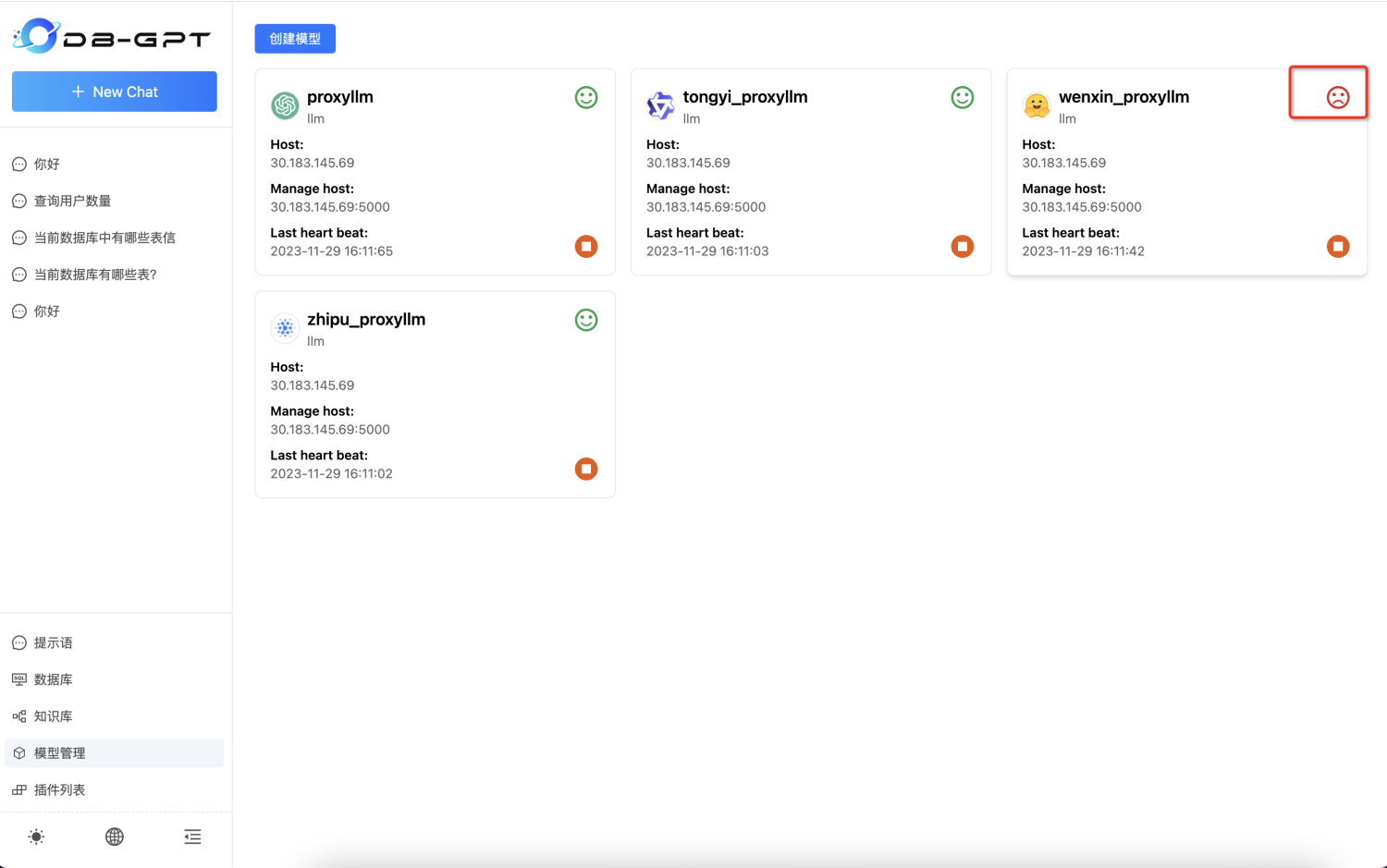
After the model is stopped, the display in the upper right corner will change.
Model Deployment
-
Open the web page, click the
model managementbutton on the left to enter the model list page, clickCreate Modelin the upper left corner, and then select the name of the model you want to deploy in the pop-up dialog box. Here we choosevicuna-7b-v1.5, as shown in the figure.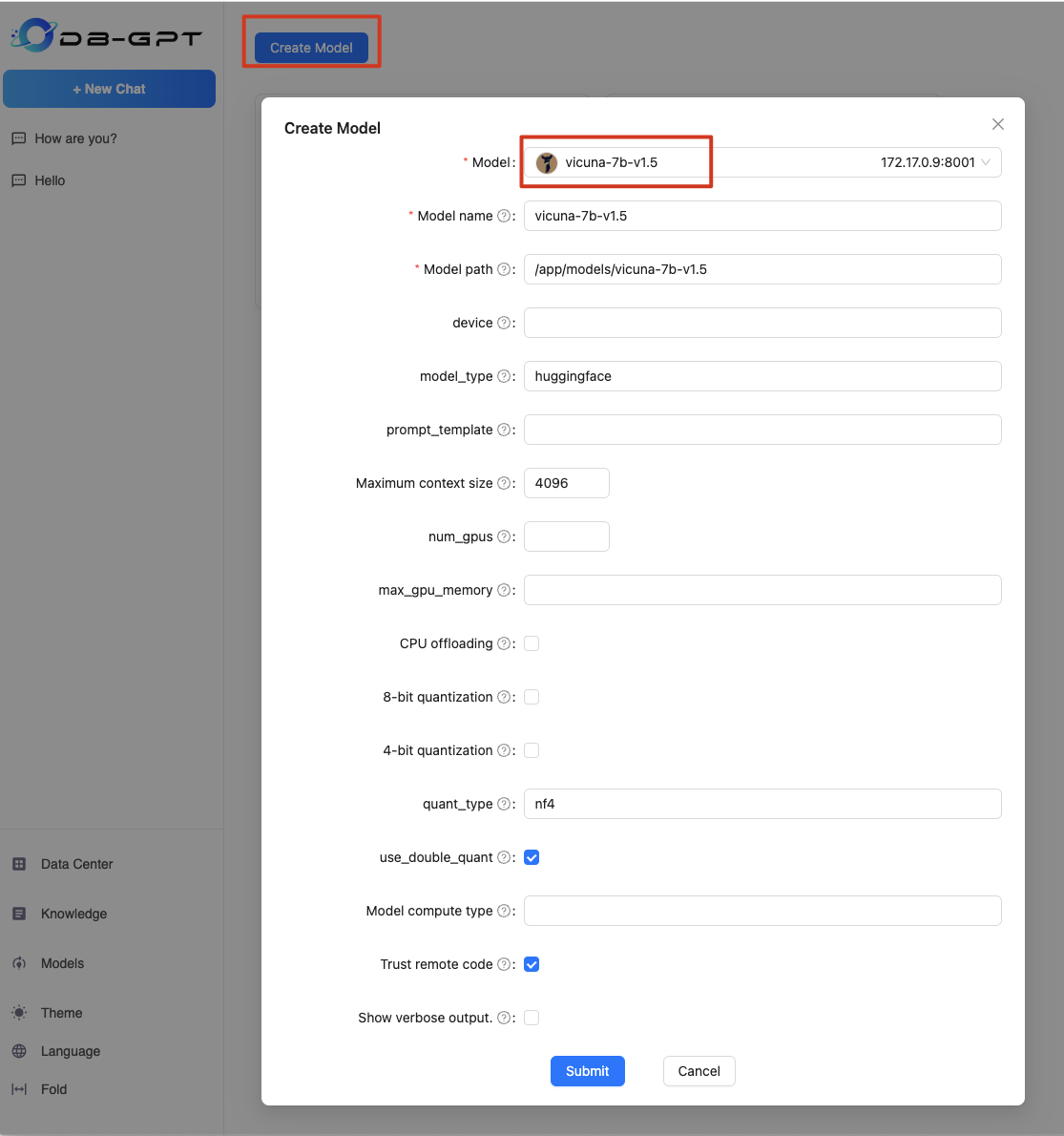
-
Select the appropriate parameters according to the actual deployed model (if you are not sure, the default is enough), then click the
Submitbutton at the bottom left of the dialog box, and wait until the model is deployed successfully. -
After the new model is deployed, you can see the newly deployed model on the model page, as shown in the figure
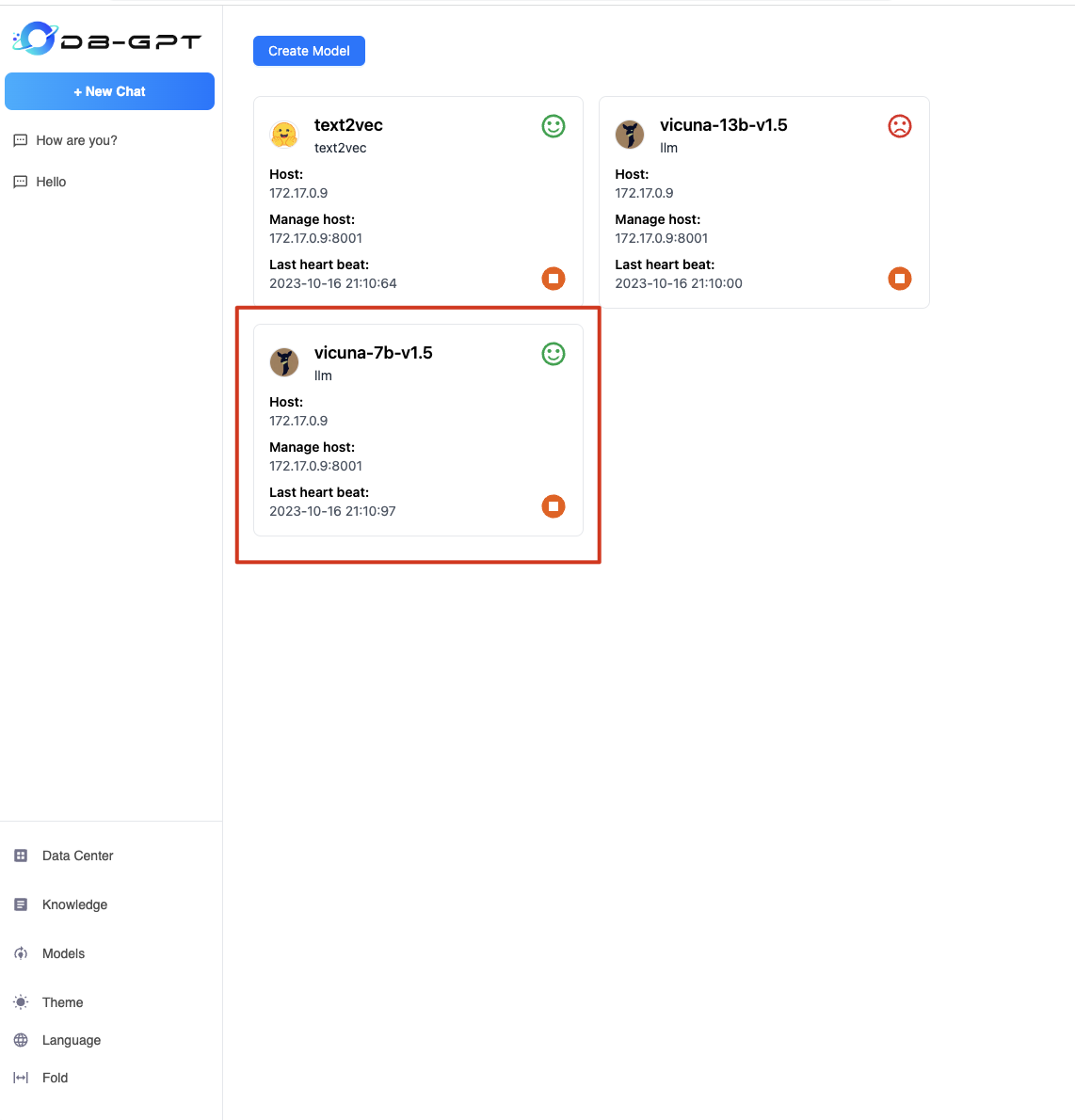
Operations and Observability
Operations and observability are important components of a production system. In terms of operational capabilities, DB-GPT provides a command-line tool called dbgpt for operations and management, in addition to the common management functionalities available on the web interface. The dbgpt command-line tool offers the following functionalities:
- Starting and stopping various services
- Knowledge base management (batch import, custom import, viewing, and deleting knowledge base documents)
- Model management (viewing, starting, stopping models, and conducting dialogues for debugging) Observability tools (viewing and analyzing observability logs)
We won't go into detail about the usage of the command-line tool here. You can use the dbgpt --help command to obtain specific usage documentation. Additionally, you can check the documentation for individual subcommands. For example, you can use dbgpt start --help to view the documentation for starting a service. For more information, please refer to the document provided below.